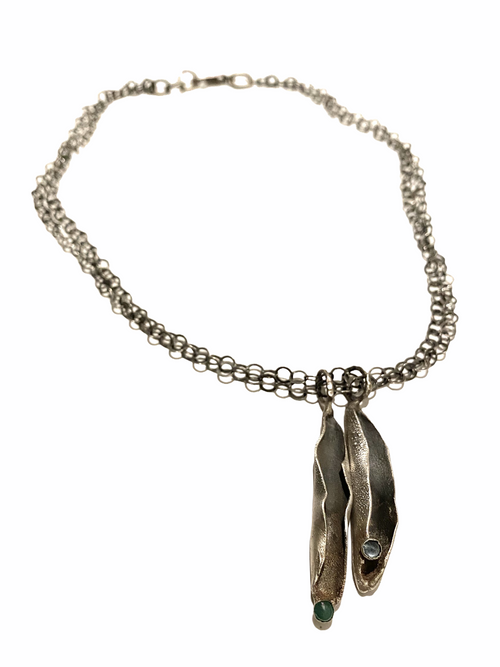
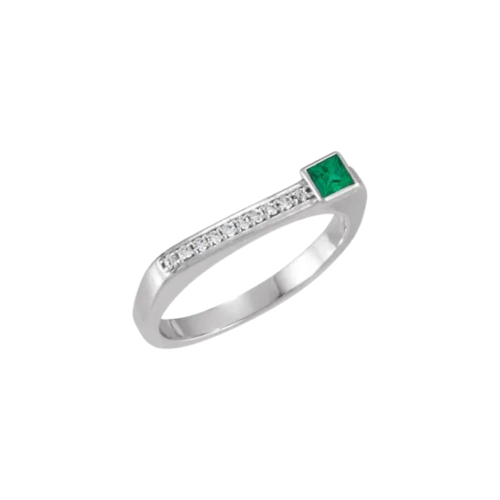
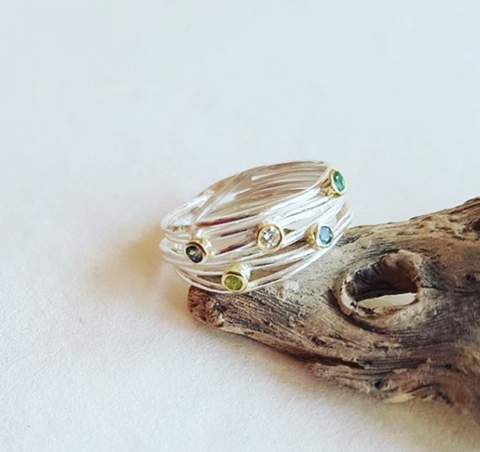
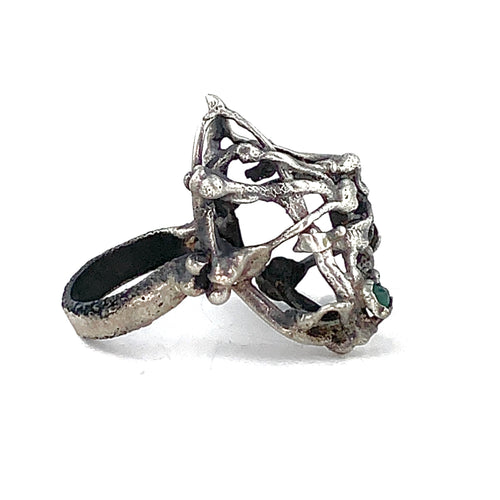
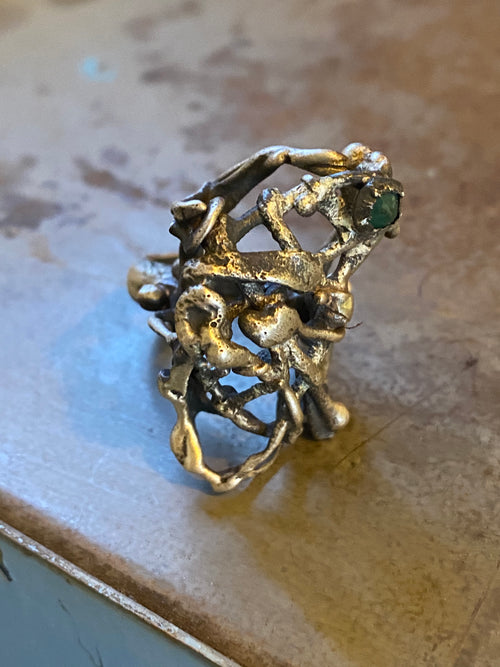
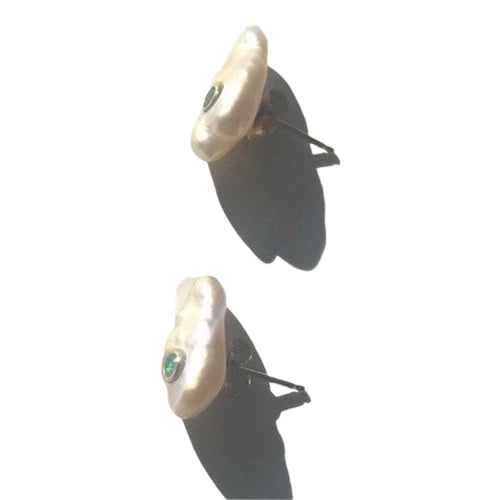
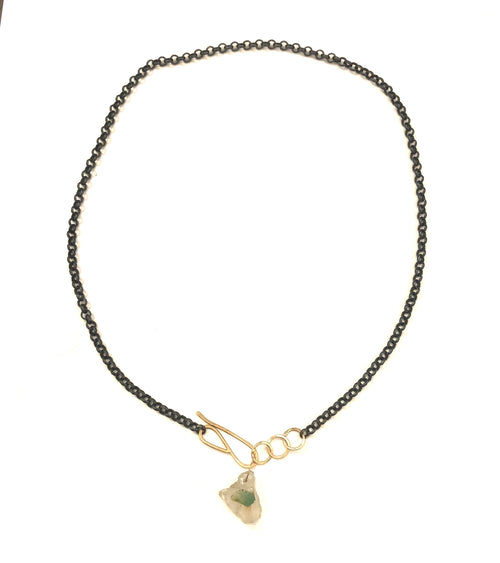
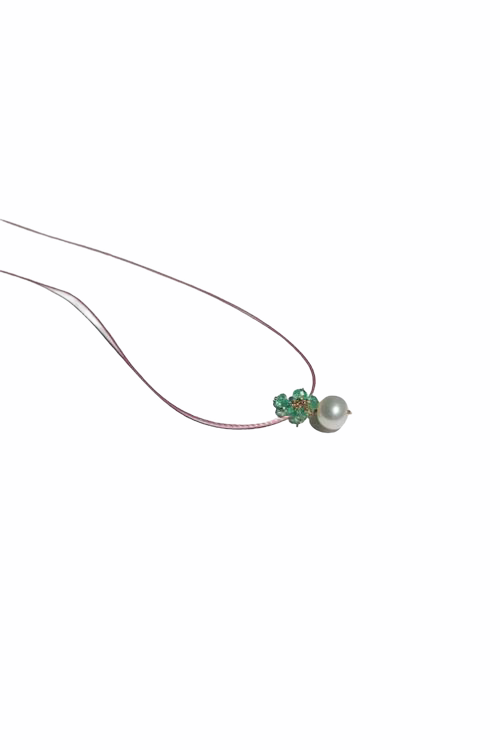
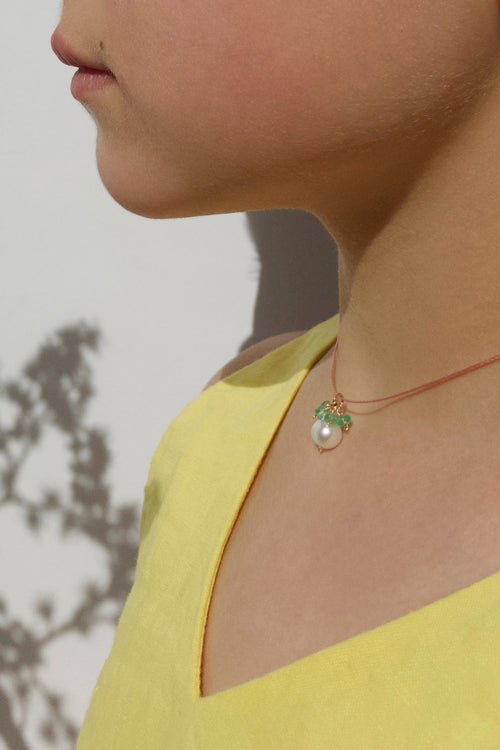
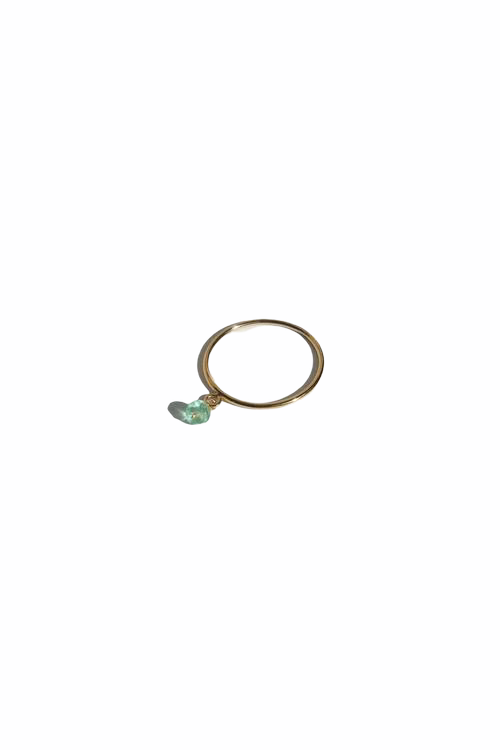
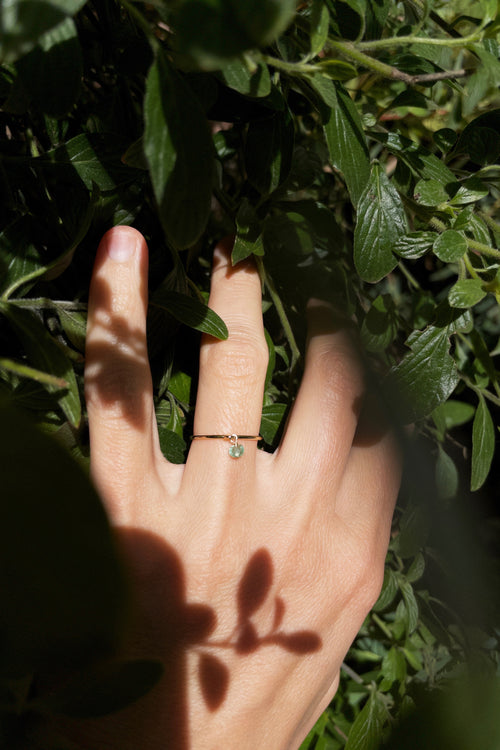
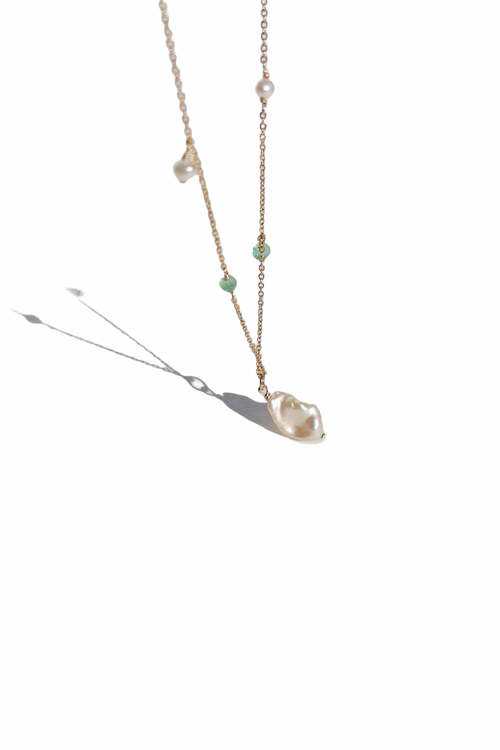
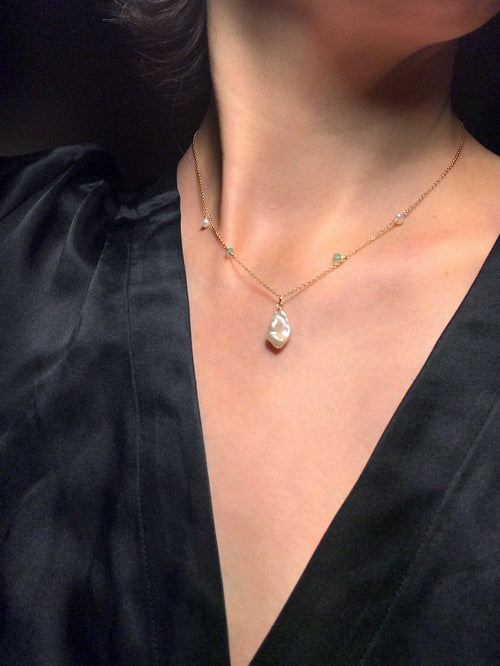
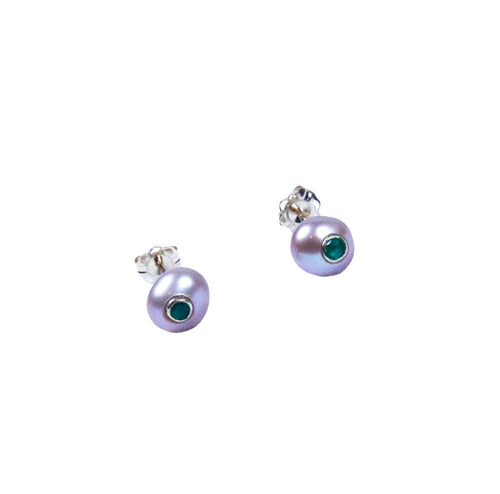
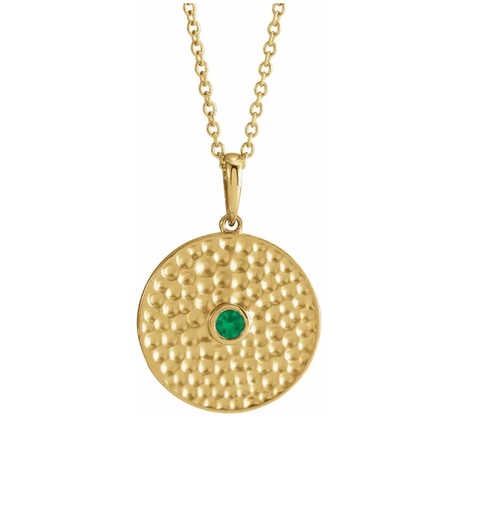
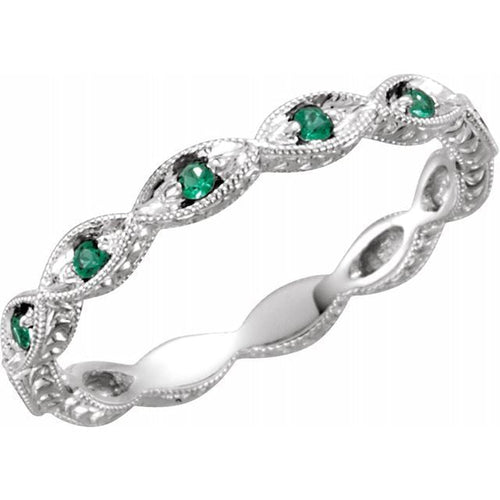
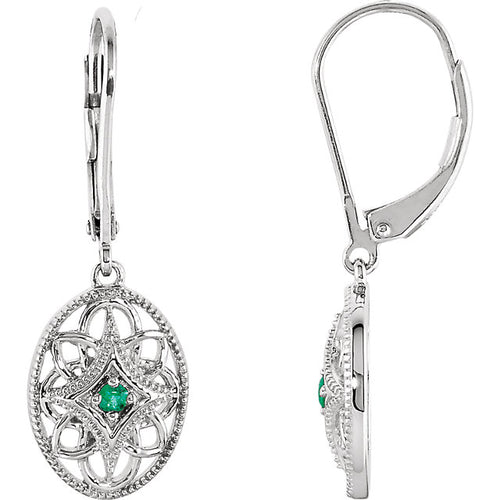
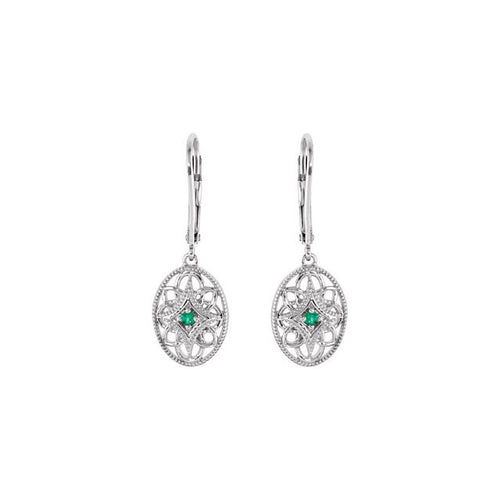
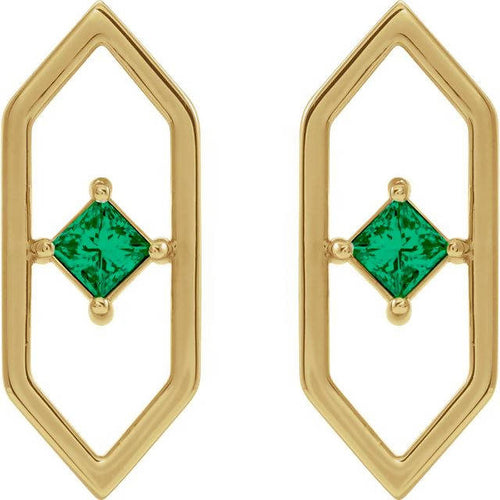
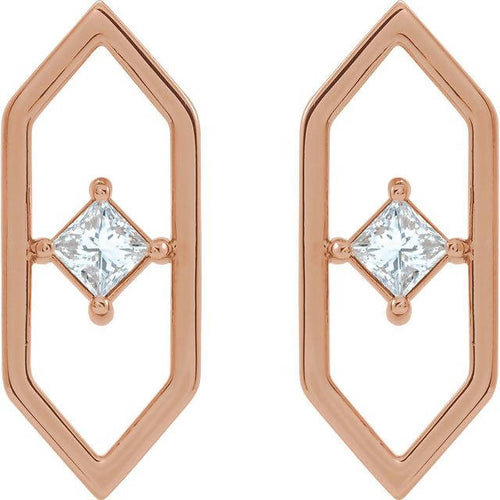
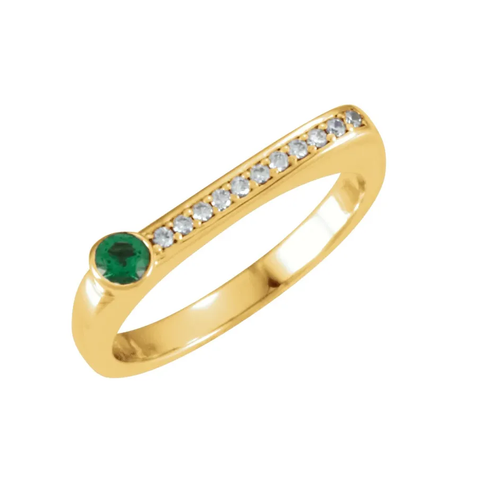
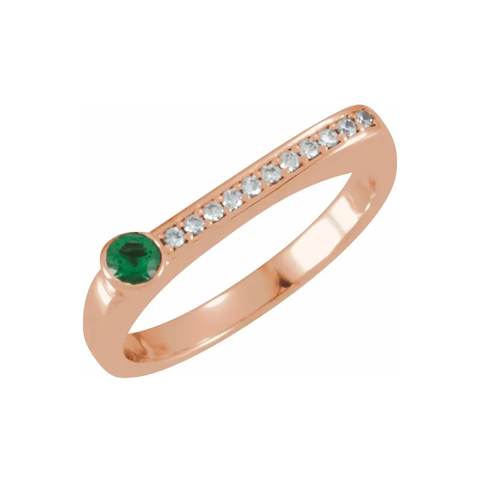
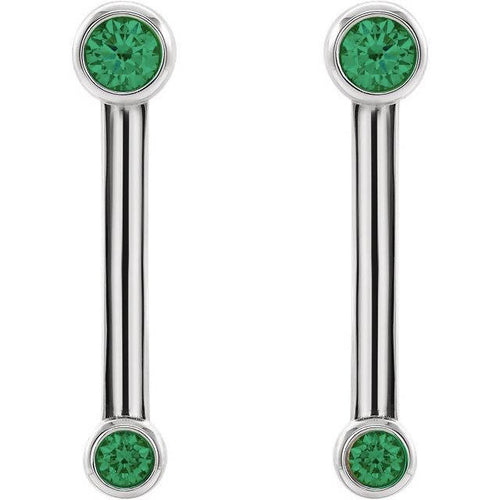
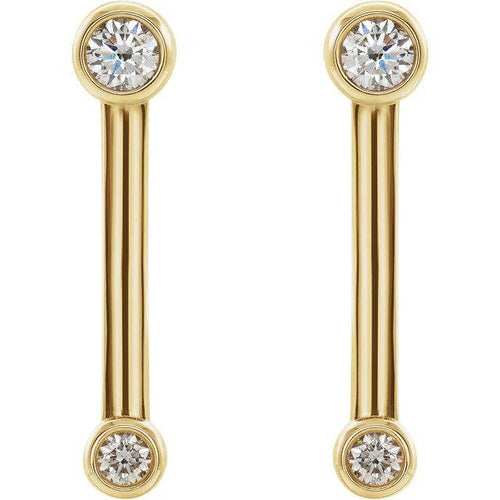
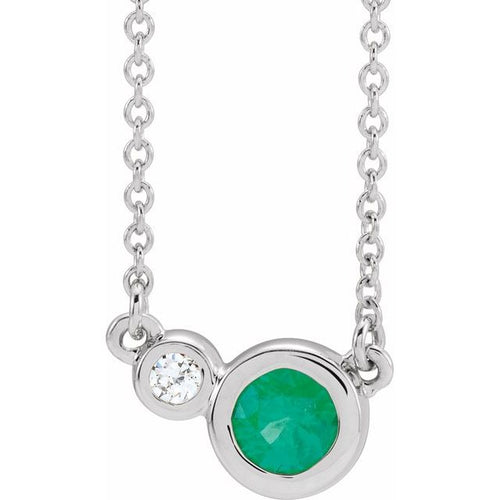
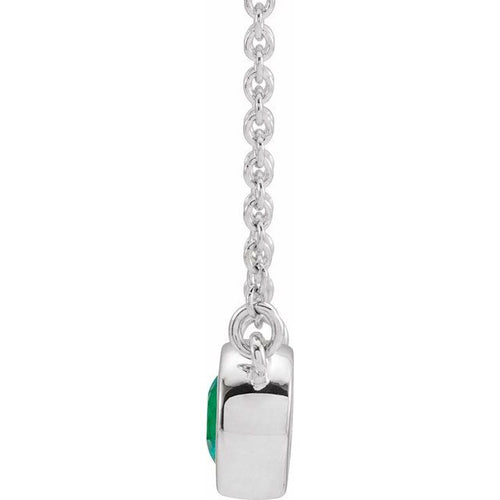
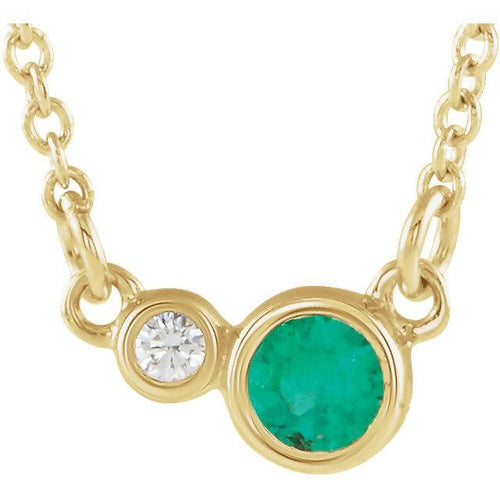
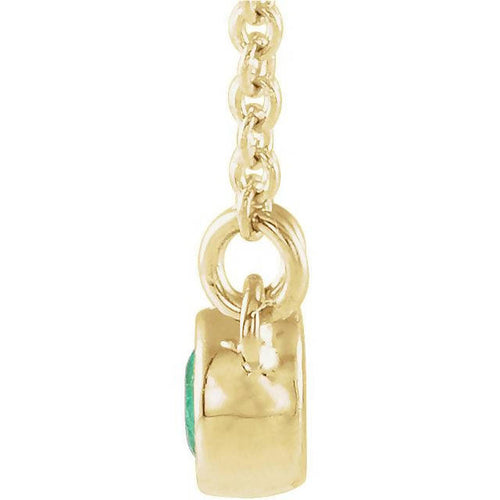
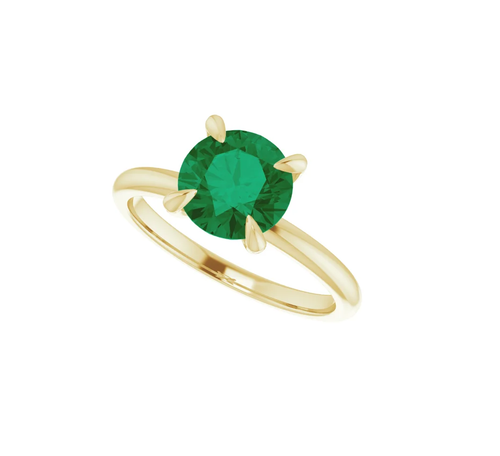
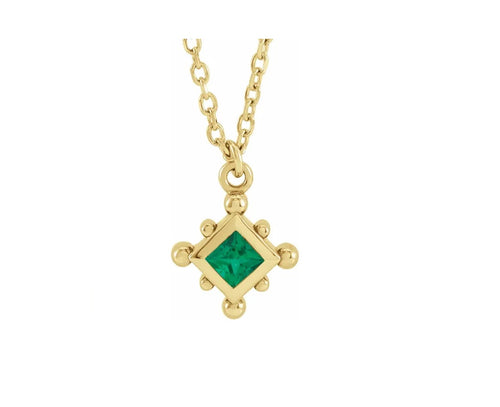
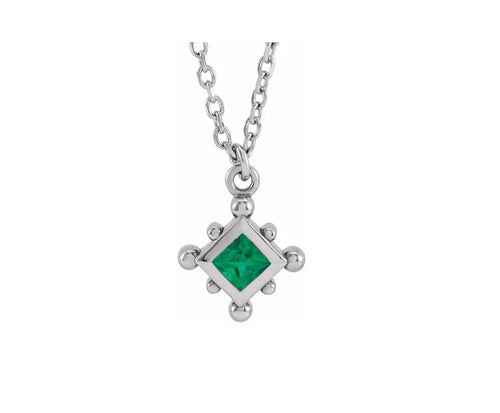
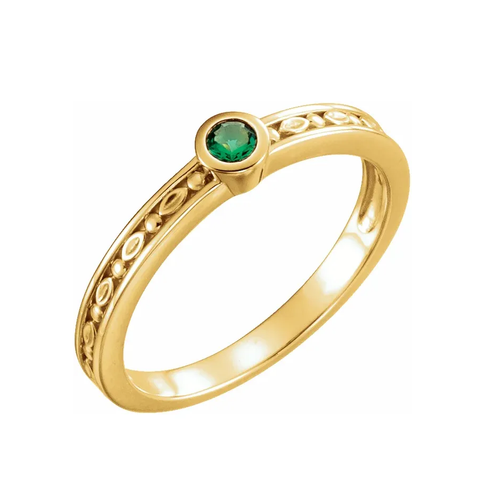
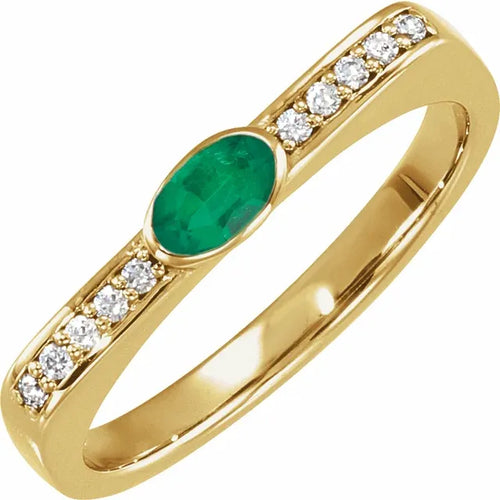
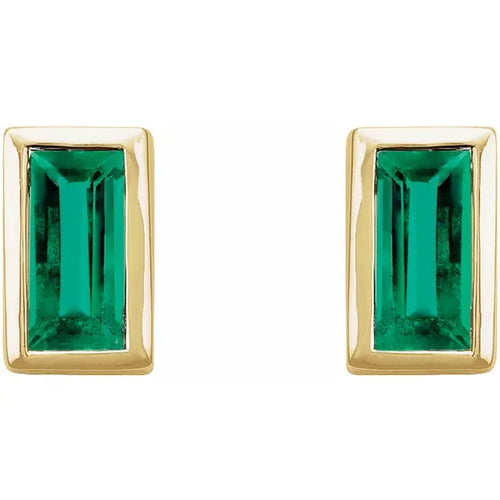
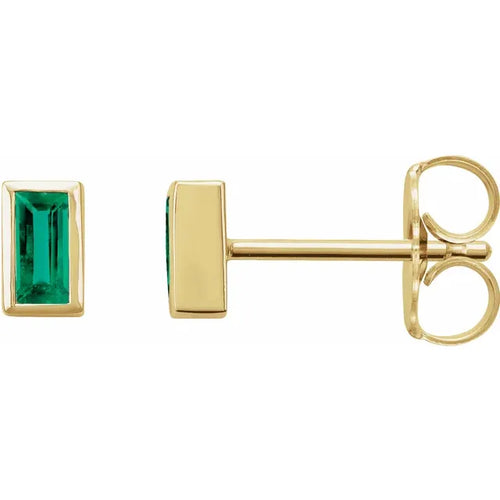
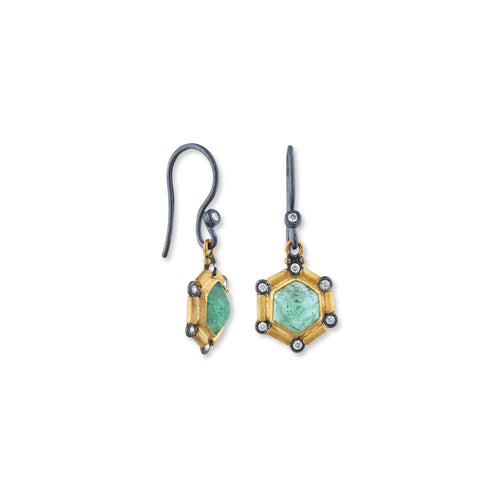
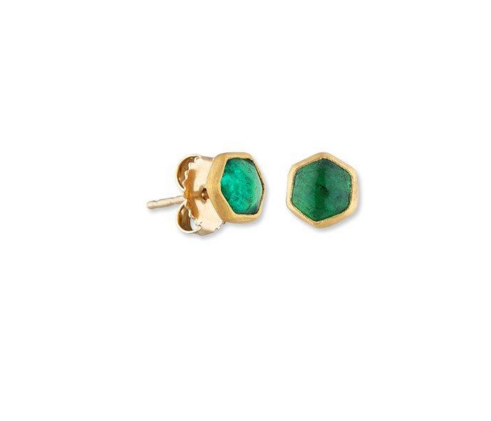
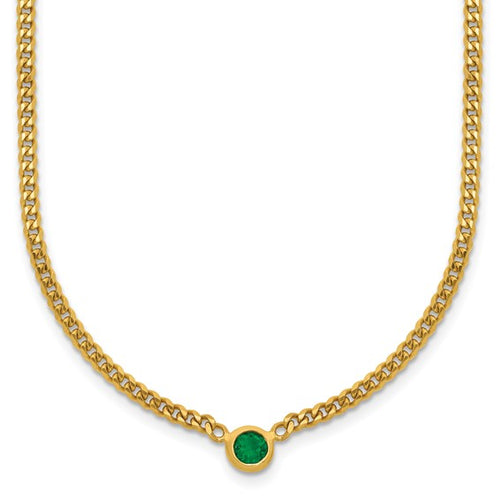
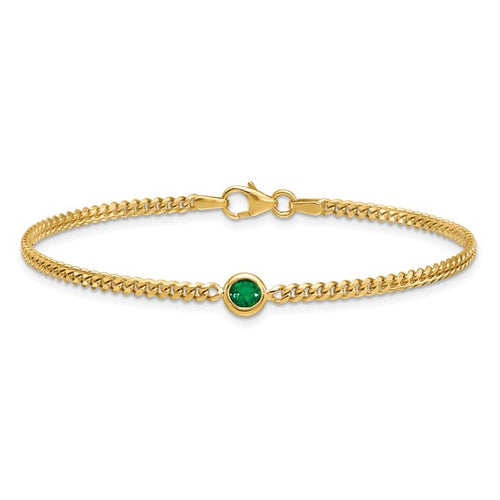
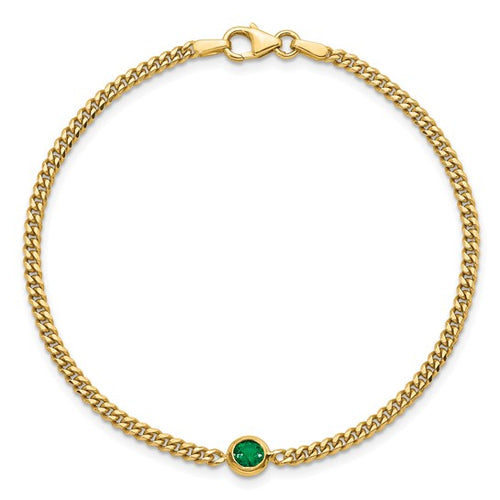
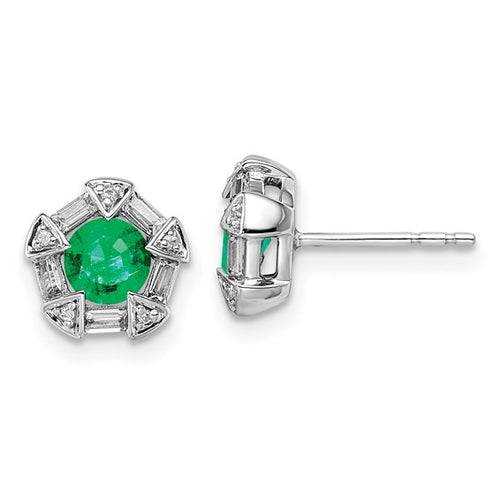
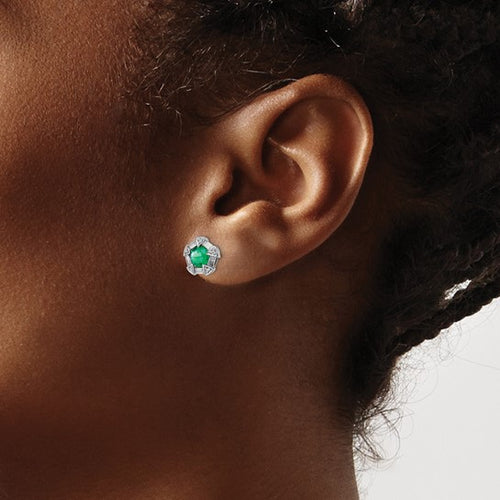
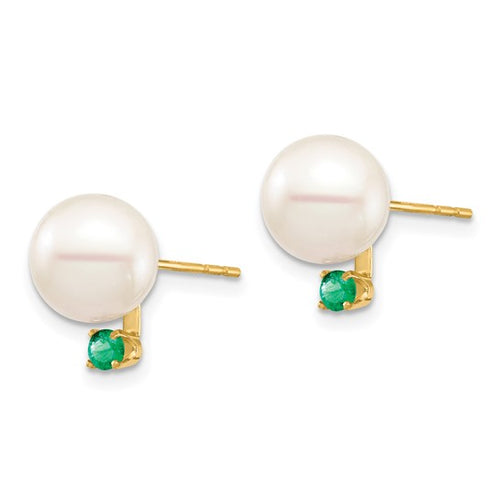
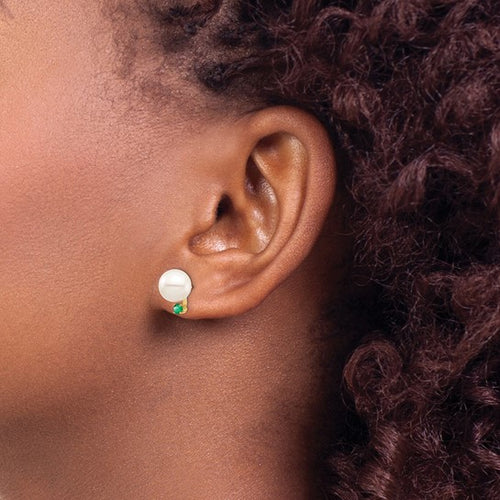
May Birthday Gifts
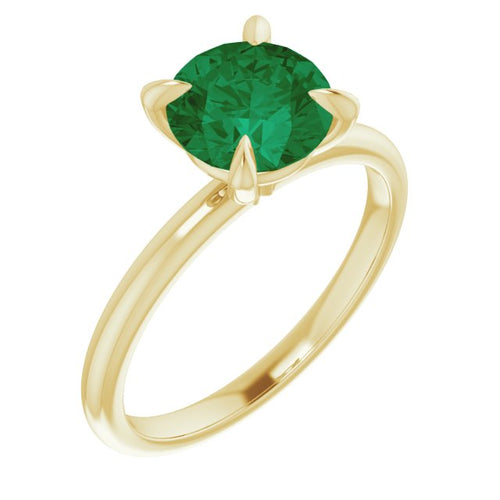
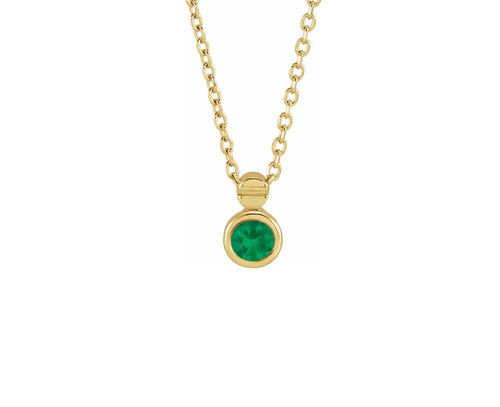
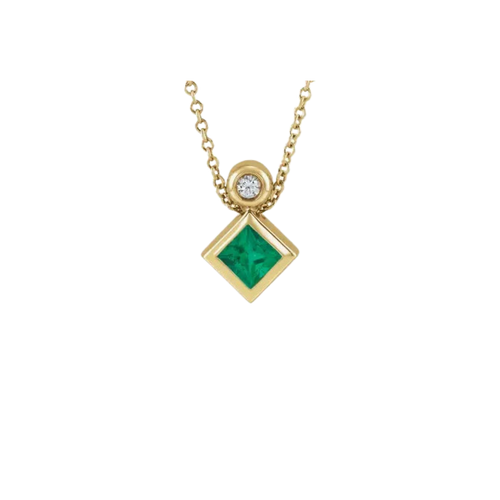
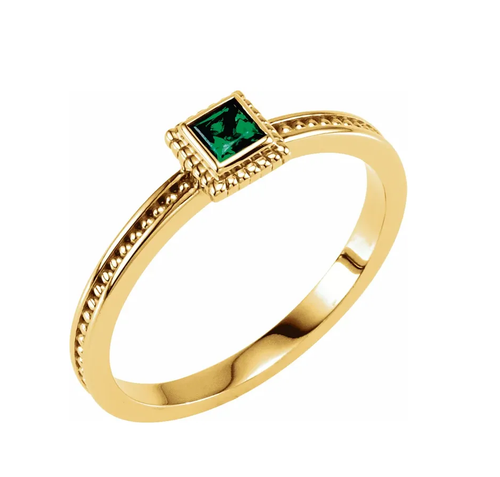
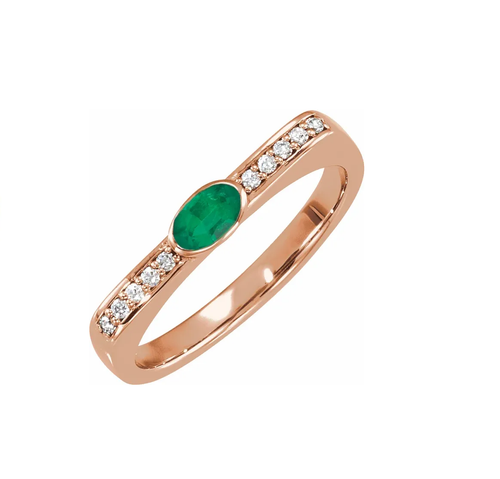
May birthstone is Emerald. Emerald is a precious gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl colored green by trace amounts of chromium and sometimes vanadium.Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds are highly included.
Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters–the four Cs of connoisseurship: color, clarity, cut and carat weight. Normally, in the grading of colored gemstones, color is by far the most important criterion. However, in the grading of emeralds, clarity is considered a close second. A fine emerald must possess not only a pure verdant green hue as described below, but also a high degree of transparencyto be considered a top gem.
In the 1960s, the American jewelry industry changed the definition of emerald to include the green vanadium-bearing beryl. As a result, vanadium emeralds purchased as emeralds in the United States are not recognized as such in the UK and Europe. In America, the distinction between traditional emeralds and the new vanadium kind is often reflected in the use of terms such as "Colombian emerald".
In gemology, color is divided into three components: hue, saturation, and tone. Emeralds occur in hues ranging from yellow-green to blue-green, with the primary hue necessarily being green. Yellow and blue are the normal secondary hues found in emeralds. Only gems that are medium to dark in tone are considered emeralds; light-toned gems are known instead by the species name green beryl. In addition, a fine emerald will be saturated and have a hue that is bright (vivid).
Emeralds tend to have numerous inclusions and surface breaking fissures. Unlike diamonds, where the loupe standard, i.e. 10× magnification, is used to grade clarity, emeralds are graded by eye. Thus, if an emerald has no visible inclusions to the eye (assuming normal visual acuity) it is considered flawless. Stones that lack surface breaking fissures are extremely rare and therefore almost all emeralds are treated ("oiled", see below) to enhance the apparent clarity. Other treatments, for example the use of green-tinted oil, are not acceptable in the trade. The relative non-uniformity motivates the cutting of emeralds in cabochon form, rather than faceted shapes. Faceted emeralds are most commonly given an oval cut, or the signature emerald cut, a rectangular cut with facets around the top edge.